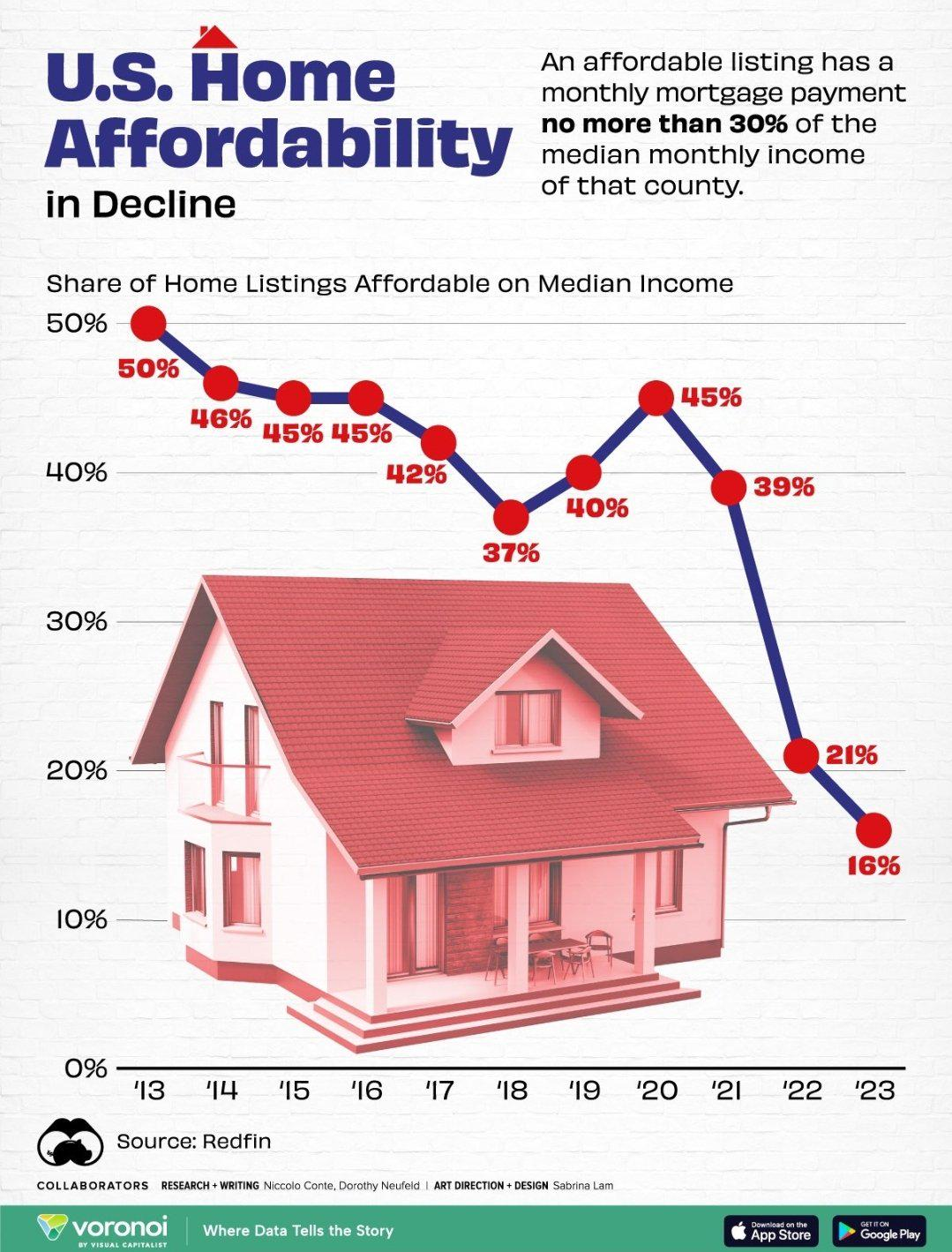
The current housing affordability crisis in the United States highlights a troubling trend that has left millions struggling to find a place to call home. As home prices continue to soar, driven in part by tight land-use regulations and escalating construction costs, the dream of homeownership is slipping further away for many Americans. Innovations in the housing market are stymied by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies, which limit the scale of new developments, ultimately curbing construction productivity. This regulatory environment not only hampers the growth of new housing units but also exacerbates homeownership challenges faced by prospective buyers. Understanding the intricacies of these issues is essential for fostering a more equitable housing landscape that benefits all.
In recent years, many communities across the United States have witnessed a significant surge in housing costs, giving rise to what many refer to as an housing affordability dilemma. This phenomenon often stems from various obstacles, including rigid land-use regulations that stifle the capacity for large-scale housing development. The collective sentiments of local residents, often encapsulated in ‘Not In My Backyard’ or NIMBY attitudes, further complicate efforts to address this critical issue. As a result, the market has struggled to keep pace with demand, leading to challenges in achieving sustainable solutions for affordable living spaces. A thorough examination of these interrelated factors is crucial to comprehending the depth of the ongoing struggle for affordable housing.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis gripping the United States presents a multifaceted challenge that is rooted in various systemic issues. The dramatic increase in home prices, with the average price of new single-family homes more than doubling since 1960, underlines the urgent need for innovative solutions. Recent studies highlight how tighter land-use regulations have played a crucial role in exacerbating this crisis, preventing builders from creating adequate housing supply to meet growing demand. This crisis affects not only potential homeowners but also has broader economic implications, as it hampers mobility and the ability of different demographics to partake in wealth creation.
Moreover, the housing affordability crisis is compounded by the strain of rising labor and material costs, which contribute to a stagnating market. Many young adults, particularly millennials and Gen Z, face homeownership challenges that were less pronounced for previous generations. Survey data indicates that a record number of younger people are delaying their first home purchase, strictly due to financial constraints exacerbated by the high cost of living and limited housing inventory. Addressing these challenges requires a reevaluation of existing policies and a commitment to fostering housing market innovation that prioritizes affordability.
Impact of Land-Use Regulations on Construction Productivity
Land-use regulations significantly influence construction productivity and, by extension, the housing market’s health. Scholars argue that stifling policies, often backed by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) sentiments, create hurdles for builders, compelling them to focus on smaller, bespoke projects instead of larger, mass-produced housing solutions. As a result, the construction industry faces a decline in both productivity and innovation, slowing the rate of home production and deepening the affordability crisis. Increased micromanagement and community input in planning processes tend to discourage large-scale projects that could alleviate pressure on housing supply.
Additionally, the historical context shows a stark contrast between past and present productivity levels in construction. For instance, between 1935 and 1970, productivity in homebuilding rose dramatically as firms capitalized on the economies of scale seen in massive developments like Levittown. Today, however, the landscape has changed, with significantly fewer large-scale projects dominating the market. Therefore, a critical look at land-use regulations signifies the need for policy reform that encourages larger, innovative construction projects while balancing community interests.
The Role of NIMBY Policies in Housing Availability
NIMBY policies have emerged as a notable barrier to increasing housing availability in the United States. These policies, often supported by local residents who prioritize their own living conditions over broader community needs, impede proposals for new developments. The resistance to multi-family housing, for example, stalls efforts to create affordable options for low- and moderate-income families. Such restrictions not only lead to a decrease in the overall housing stock but also inflate existing property values, contributing further to the housing affordability crisis.
In the face of stringent NIMBYism, the construction sector struggles to adapt, often resulting in smaller firms being the only builders left in the field. The consequence is a cycle where smaller projects yield fewer housing options that do not adequately meet the needs of the population. A shift in public perception and policy is vital to ensure a more equitable approach to housing development, one that recognizes the importance of diverse living arrangements and embraces innovative solutions for sustainability.
Housing Market Innovation: Pathways to Affordability
To effectively address the housing affordability crisis, the sector must embrace innovation that redefines traditional construction and development practices. This includes adopting new technologies that streamline construction processes, improving efficiency, and ultimately lowering costs. For instance, modular construction techniques and prefabricated homes can significantly reduce both time and expenditure, allowing for faster delivery of housing units to the market.
Moreover, fostering partnerships between private builders and local governments can lead to creative zoning reforms that promote mixed-use developments. Such collaborations might involve flexible land-use policies that incentivize the development of affordable housing options without compromising the quality of life for existing residents. Housing market innovation is essential not only for increasing supply but also for ensuring that the new housing produced meets the diverse needs of today’s population.
Homeownership Challenges Facing Younger Generations
Today’s younger generations grapple with unprecedented homeownership challenges, many of which stem from an environment of rising costs juxtaposed with stagnant wages. As housing prices climb beyond reach, they are forced to navigate financial barriers, including student loan debt and the lack of affordable rental options. Consequently, many millennials and Gen Z individuals are postponing their dreams of homeownership, impacting their long-term financial stability and wealth accumulation potential.
In addition to economic factors, cultural shifts play a role in complicating the path to homeownership. There is often a perception of homeownership being an essential milestone of adulthood, yet the contemporary housing market conditions make it increasingly difficult to achieve. It emphasizes the need for policies that not only facilitate affordability but also address intergenerational wealth transfers, ensuring equitable opportunities for future homeowners.
The Intergenerational Transfer of Housing Wealth
The concept of intergenerational transfer of housing wealth highlights a growing disparity in home equity among different age cohorts, revealing broader economic and social consequences. The stark drop in home equity among younger earners since the 1980s illustrates how the accumulation of housing wealth has significantly shifted, benefitting older generations while leaving younger individuals with limited opportunities in the property market. As data indicates, median earners in their 30s and 40s hold a fraction of the equity compared to their counterparts from thirty years ago.
This disparity not only influences individual financial situations but also has wider implications for economic mobility and social equity. Unless addressed through innovative policies targeting both housing supply and affordability, this transfer of wealth may continue to reinforce socio-economic divides, leaving younger generations at a disadvantage as they strive for financial independence. Therefore, creating viable strategies to support equitable homeownership is crucial in halting this cycle.
Examining Construction Patent Activity Trends
The decline in construction patent activity following the 1970s serves as a key indicator of stagnation within the industry, contrasting sharply with advancements seen in manufacturing. Historically, the construction sector witnessed vibrant innovation that contributed to growing productivity levels and a heightened rate of home building. However, after the surge in land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, the rate of patents declined, reflecting a stagnation in new practices and technologies within this essential sector.
Understanding these trends highlights the deficient investment in research and development in construction compared to other industries, signaling a crucial area for policy intervention. Encouraging innovative practices within the construction industry can pave the way for increased efficiency and lower costs, ultimately contributing to a healthier housing market. Prioritizing technological advancements and incentivizing patent activity could spur a renaissance in the sector, offering promise in alleviating the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
Moving Forward: Policy Reforms for Housing Affordability
To effectively combat the persistent housing affordability crisis and promote a more accessible market, comprehensive policy reforms are indispensable. Policymakers must focus on amending restrictive land-use regulations and encouraging developments that cater to diverse housing needs. By implementing more flexible zoning laws, local governments can help facilitate larger-scale building projects, allowing the construction industry to regain its historical productivity levels while also providing affordable housing options.
In addition, integrating housing policy with economic strategies aimed at supporting younger generations is crucial. Programs aimed at reducing the financial burdens of first-time homebuyers, such as down payment assistance initiatives and favorable loan policies, can empower a new cohort of owners and stimulate economic growth. Through thoughtful reforms, the landscape of homeownership can be transformed, offering renewed hope and stability in the housing market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of the housing affordability crisis in the U.S.?
The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. can be attributed to several factors, including increasing labor and material costs, restrictive land-use regulations, and NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies. These regulations limit construction productivity and innovation, leading to fewer affordable housing options and making homeownership increasingly unattainable for many Americans.
How do land-use regulations contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by hampering construction productivity. These regulations often restrict the size and type of developments, leading to smaller projects that are less efficient. Consequently, builders face higher costs, which are passed on to consumers, exacerbating the lack of affordable housing in the market.
What is NIMBYism and how does it affect housing affordability?
NIMBYism, or Not In My Backyard policies, is a social phenomenon where residents oppose local development projects, often due to perceived negative impacts on their community. These attitudes contribute to the housing affordability crisis by limiting the construction of new housing projects, thereby reducing supply and driving up prices, making homeownership increasingly out of reach for many.
What role does construction productivity play in addressing the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity is crucial in tackling the housing affordability crisis. Higher productivity leads to more efficient building processes, which can lower costs and increase the availability of affordable housing. However, current land-use regulations and small project sizes hinder productivity, thus escalating home prices and exacerbating the crisis.
How do homeownership challenges relate to the housing affordability crisis?
Homeownership challenges are intricately linked to the housing affordability crisis, as soaring home prices, driven by inadequate supply and high construction costs, make it difficult for many individuals to enter the housing market. The resultant financial strain affects homeownership rates, particularly among younger and middle-income families, thereby widening the wealth gap.
In what ways can housing market innovation help solve the affordability crisis?
Housing market innovation can help alleviate the affordability crisis by introducing new building technologies, designs, and financing methods that reduce costs and increase efficiency. Innovations such as modular construction and sustainable building practices can lead to more affordable housing options that better meet the needs of various communities while complying with local regulations.
What impact do economic disparities have on homeownership in light of the housing affordability crisis?
Economic disparities significantly affect homeownership rates amid the housing affordability crisis. With rising housing costs, those in lower income brackets struggle to find affordable options, while wealthier individuals benefit from property value increases. This disparity not only limits access to homeownership for many but also perpetuates cycles of poverty and inequality within communities.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The price of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, placing ownership out of reach for many Americans. |
| NIMBY Policies | ‘Not in my backyard’ (NIMBY) land-use regulations have harmed builders’ productivity and innovation, further driving up housing prices. |
| Decline in Builder Productivity | Construction productivity fell by 40% from 1970 to 2000, contrasting with continued growth in other sectors, like auto manufacturing. |
| Impact of Land Use Regulations | Increased land-use regulations have limited construction project sizes, leading to smaller firms that lack the capacity for economies of scale. |
| Historical Perspective | Historically, large projects (e.g., Levittown) produced homes efficiently but have become rare due to regulatory constraints. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations hold significantly less housing wealth compared to older generations, highlighting economic disparities. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue faced by many Americans today, exacerbated by restrictive land-use regulations and declining productivity in the construction sector. While the U.S. economy has seen significant productivity gains in various industries, housing has lagged behind, mostly due to stringent NIMBY policies that hinder the development of larger, cost-effective housing projects. As a result, the price of homes has surged, effectively locking many individuals and families out of homeownership. Without addressing these regulatory challenges, the trend of escalating housing costs is likely to persist, further widening the gap between property owners and non-owners.