Corporate tax cuts have become a hot-button issue, particularly in the wake of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which significantly altered the landscape for business taxation in the United States. As Congress braces for a tax showdown in 2025, the implications of these cuts on corporate tax revenue and economic growth are under intense scrutiny. Economists like Gabriel Chodorow-Reich have analyzed the economic impact of tax cuts, particularly how they relate to business investment tax policy and wages. While proponents argue that these tax reductions stimulate investment, critics point to the substantial loss in tax revenue and question their overall effectiveness. As a new wave of debate unfolds, understanding the balance between corporate taxes and fiscal responsibility has never been more critical.
Tax reductions for corporations, often termed business tax relief, have sparked considerable dialogue amid electoral campaigns and economic discourse. Following the enactment of the 2017 tax reform, the conversation around corporate fiscal policies has evolved, raising questions about their influence on economic growth and investment behaviors. Analysts, including prominent economists like Chodorow-Reich, evaluate the nuances of these fiscal adjustments, emphasizing their role in shaping corporate profitability and government revenue. The discussion not only focuses on the direct benefits to businesses but also explores the broader economic implications for the labor market and public finances. As the expiration of several key provisions approaches, stakeholders from all sectors are closely watching how these decisions will ultimately reshape the economic landscape.
Understanding the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) marked a significant overhaul of the U.S. tax code, slashing corporate tax rates from 35% to 21%. This reduction was aimed at making the American economy more competitive globally, particularly as other countries reduced their tax rates. However, it also sparked a contentious debate over its economic rationality and social implications. Some proponents argue that lower tax rates stimulate business investments and innovation, which could theoretically lead to job creation and wage growth. Opponents, however, raise concerns about the long-term impacts on federal revenue and economic inequality.
Moreover, the TCJA introduced several provisions that allowed companies to immediately write off investments in capital and research. These immediate expensing features were expected to drive higher levels of business investment, thus having a positive ripple effect on economic growth. Gabriel Chodorow-Reich’s research emphasizes the mixed outcomes of these policy changes—while some firms increased their investments significantly due to the tax breaks, the broader impacts on wages and overall economic health have been debated, indicating that tax cuts do not automatically equate to economic prosperity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main effects of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act on corporate tax revenue?
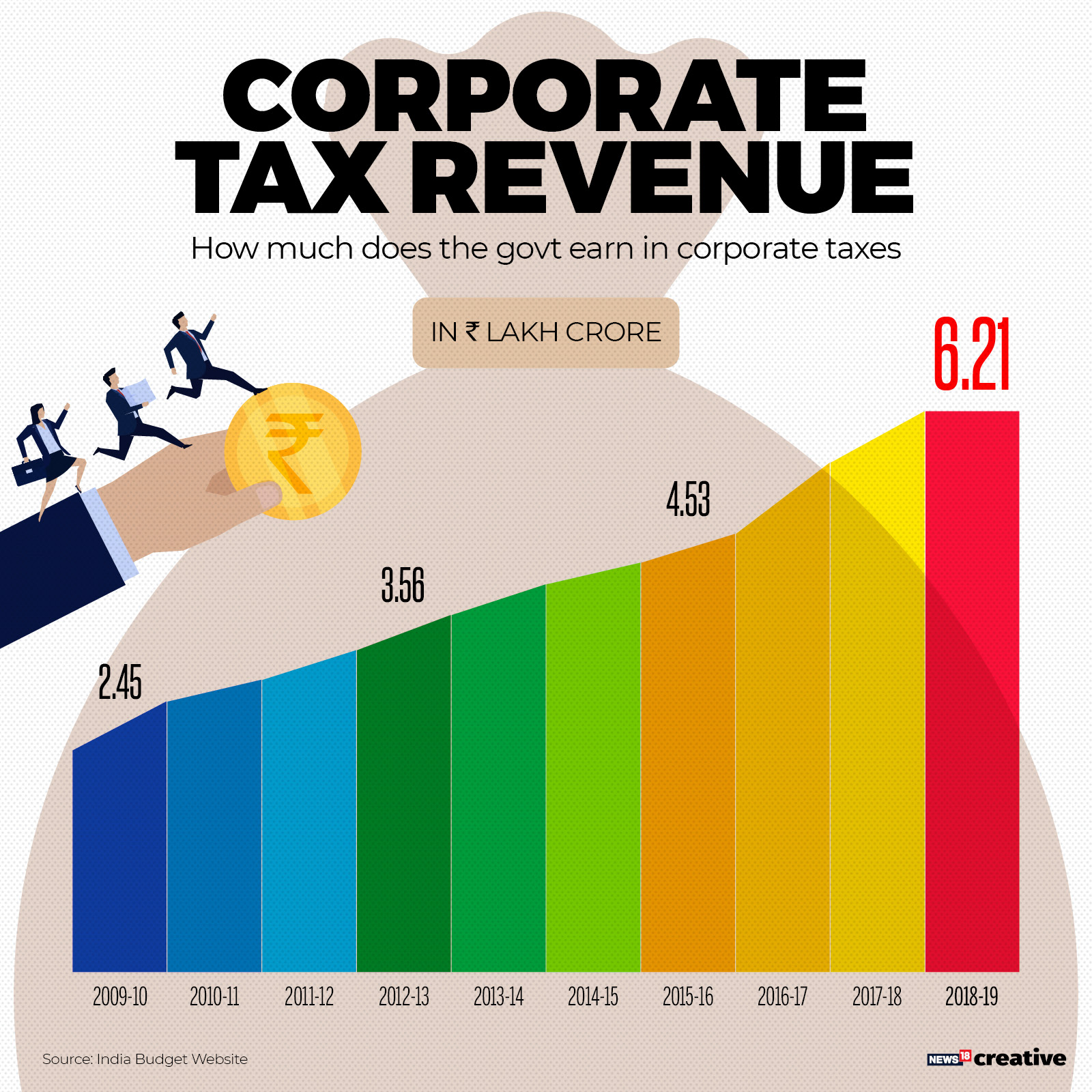
The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) led to a significant initial drop in corporate tax revenue by about 40%. Over time, however, corporate tax revenue began to recover, eventually surpassing expectations as business profits surged due to various economic factors. This indicates a complex interplay between corporate tax cuts and the overall economic environment.
How did corporate tax cuts affect business investment after the TCJA?
Following the implementation of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, there was a notable increase in capital investments by approximately 11%. This was largely driven by specific provisions that allowed accelerated expensing, proving more effective for driving investment than traditional rate cuts.
What did Gabriel Chodorow-Reich conclude about the economic impact of corporate tax cuts?
Gabriel Chodorow-Reich’s analysis of the TCJA showed that while there were some modest increases in wages and business investments, the overall economic impact does not fully support the idea that tax cuts alone can stimulate significant economic growth without accompanying reforms in other areas.
How did the TCJA change corporate tax rates, and what was its intended goal?
The TCJA permanently reduced the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, aiming to make U.S. businesses more competitive globally and to encourage domestic investment. However, this substantial cut was expected to decrease federal corporate tax revenue significantly.
What controversies surround the corporate tax cuts implemented by the TCJA?
The corporate tax cuts from the TCJA have been contentious, with debates centering on their effectiveness in stimulating long-term economic growth, the actual increase in wages, and the substantial loss in tax revenue that accompanied these cuts, leading to polarized opinions among economists.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Corporate tax cuts in the TCJA were reduced from 35% to 21%. This change was intended to stimulate growth but resulted in a significant drop in federal tax revenue. |
| Current political discourse shows a split between those advocating for increased corporate taxes versus further cuts. |
| Research indicates moderate increases in business investments and wages due to the tax cuts. |
| Expired provisions of the TCJA proved to be more effective in driving investment than the statutory cuts themselves. |
| Corporate tax revenue initially dropped but began recovering, fueled by unexpected surges in business profits. |
| Ongoing studies are necessary to fully understand the long-term impact of corporate tax cuts on wages and investment. |
Summary
Corporate Tax Cuts represent a pivotal discussion point as Congress prepares for potential changes in 2025. The recent analysis of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act highlighted mixed outcomes from the corporate tax reductions, revealing modest gains in investments and wages against a backdrop of significant federal revenue losses. As the expiration of provisions looms, voters and leaders alike are debating whether to renew tax cuts or implement increases. Understanding the nuanced effects of these tax policies is crucial for informed decision-making in the evolving economic landscape.