The impact of AI on the labor market is shaping up to be a significant force of change, as recent studies reveal transformative trends influenced by emerging technologies. Researchers, including noted economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, suggest that artificial intelligence is initiating waves of occupational churn, affecting job availability across various sectors. While many feared job polarization leading to a decrease in middle-wage roles, data indicates a shift favoring high-skill positions, particularly in STEM jobs. This technology disruption is not limited to mere job displacement; it’s also fostering an increased demand for skilled professionals, creating a dynamic labor landscape. As we delve deeper into these AI and employment trends, it becomes clear that the future of work will be intricately intertwined with technological advancements.
Exploring the effects of artificial intelligence on workforce dynamics unveils a pressing issue in today’s economy. Analysts and scholars are keenly observing the changes that technology instigates, leading to a phenomenon often referred to as labor market upheaval. The discussion spans various themes, including the rise of skill-intensive employment and the paradox of job loss in traditional roles. Notably, professions in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) are uniquely positioned to thrive amid these shifts. As society adapts to this new wave of technological innovation, it is crucial to understand the broader implications for employment and career development.
The Evolution of the Labor Market: A Historical Perspective
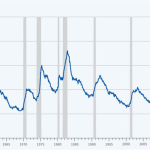
Over the past century, the U.S. labor market has undergone numerous transformations driven by technological advancements. Researchers like economists David Deming and Lawrence Summers have delved deep into this evolutionary process, examining how various breakthroughs, from electrical systems to personal computing, have shaped labor dynamics. Their studies showcase a historical perspective of ‘occupational churn,’ revealing distinct patterns of employment and industry share, which illustrate the persistent impact that technological innovation has had on job structures.
In particular, the time frame from 1990 to 2017 was marked by stability, where concerns about robots replacing human workers appeared exaggerated. During this period, shifts in employment actually plateaued, leading many to believe that automation was not leading to significant disruption. However, as Deming and Summers uncovered recent changes in data post-2019, it prompted a renewed focus on how emerging technologies—especially AI—are redefining the landscape. The notion of volatility in the job market they’ve observed draws attention to the adaptive nature of employment and underscores the historical significance of breakthrough technologies in reshaping economies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI causing technology disruption in the labor market?
AI is a key factor in technology disruption within the labor market, as it leads to shifts in job structure and employment patterns. Research indicates that since 2019, AI has contributed to significant changes, particularly in boosting demand for STEM jobs and advancing job polarization, where high-skilled, high-income positions are increasingly prevalent.
What are some examples of occupational churn related to AI and employment?
Occupational churn refers to the ongoing changes in job roles and industries as a result of AI and technological advancements. Specifically, we’ve seen a decline in low-paid service jobs since 2019, as AI automates tasks traditionally performed by humans, altering the job landscape significantly.
Is AI leading to job polarization in the labor market?
Yes, AI is driving job polarization, resulting in a labor market divide where high-paying, skilled jobs are on the rise while middle-income roles struggle. The shift towards automated processes enhances the demand for highly trained individuals in STEM fields, reshaping wage distributions.
What trends are emerging in STEM jobs due to AI’s impact on the labor market?
AI has spurred notable increases in STEM job opportunities, with the percentage of jobs in these fields rising from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. This represents a nearly 50% increase, highlighting the growing importance of technical expertise as AI transforms various industries.
How has AI influenced the volatility of the labor market historically?
Historically, AI has introduced significant volatility in the labor market, particularly seen in the data from 1950s to the 1970s with breakthrough technologies. Recent findings indicate a resurgence of this volatility, driven by AI advancements and changing job requirements, especially post-2019.
What role does AI play in the recent decline of retail jobs?
AI has significantly contributed to the decline of retail jobs, with a notable drop from 7.5% to 5.7% of the labor market between 2013 and 2023. This reduction is largely due to the rise of e-commerce, which has rapidly adopted AI technologies to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
How is automation linked to shifts in job requirements in various sectors?
Automation, particularly due to AI, is leading to heightened expectations for productivity among knowledge workers. Companies are increasingly leveraging AI technologies, which necessitates that employees adapt quickly and demonstrate greater efficiency in their roles, transforming traditional job responsibilities.
What should workers consider about AI’s impact on the future of employment?
Workers across all sectors should recognize AI’s empowering potential along with its risks. While AI can enhance productivity, it also poses a threat of job displacement, particularly for roles where tasks can be automated. Therefore, continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies are critical for future job security.
| Key Trends | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization Ending | Shift from a barbell pattern to a focus on high-compensated jobs as labor market dynamics change. |
| Rise of STEM Jobs | Significant increase in science, technology, engineering, and math jobs, growing from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Work | Occupational churn reveals a decline in low-paid service jobs since 2019, possibly due to AI, higher wages, and COVID-19 disruptions. |
| Job Loss in Retail Sales | Retail jobs decreased by 25% from 2013 to 2023, largely influenced by the rise of e-commerce and AI. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly apparent, with research indicating significant shifts resulting from technological advancements over the past century. As new trends emerge, such as the decline of job polarization and an increase in STEM occupations, it is clear that AI is reshaping the workforce landscape. Despite initially stable employment patterns, recent findings suggest a burgeoning transformation as the economy adapts to AI integration, necessitating a reevaluation of job structures and skills required in various industries.